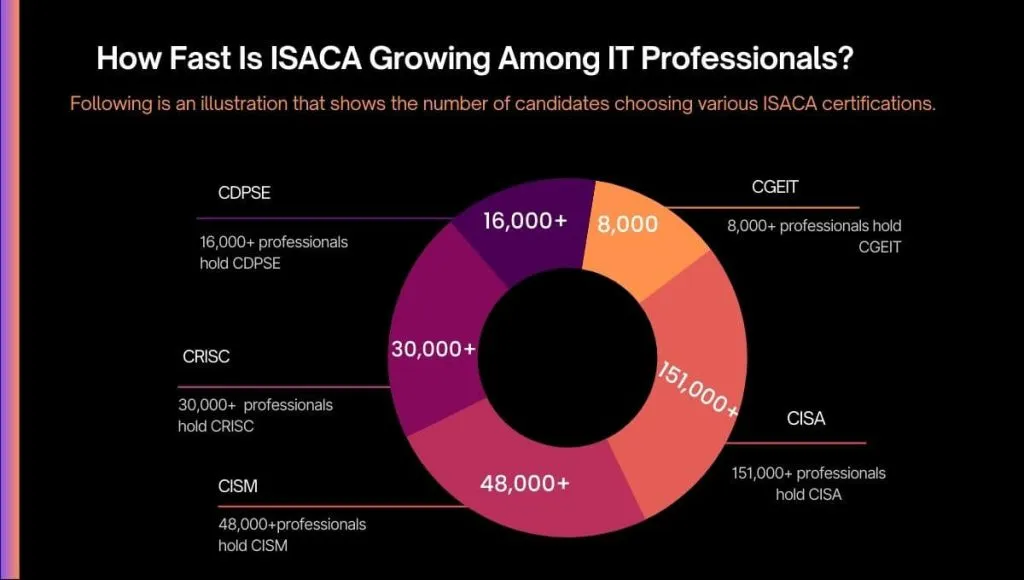
In every industry today—finance, healthcare, technology, energy, government, and beyond—organizations operate under growing pressure to manage risk, protect data, meet regulatory expectations, and maintain operational integrity. Governance professionals are the individuals who hold these systems together. They shape internal controls, evaluate risks, define security policies, and ensure that organizations behave ethically and responsibly.
ISACA certifications play a transformative role in this space, strengthening governance careers from early levels to high-level advisory positions. Professionals researching governance credentials usually begin by exploring pathways such as CISA, CISM, CRISC, and CGEIT through detailed vendor listings like https://certempire.com/vendor/isaca/ — a useful reference for understanding how each certification aligns with governance responsibilities.
As organizations transition into cloud ecosystems, hybrid operations, AI adoption, and global regulatory complexity, ISACA certifications have become more important than ever. They validate a professional’s ability to guide decisions, protect assets, manage enterprise-wide risks, and build frameworks that support sustainable business operations.
What follows is a deep, role-based exploration of how ISACA certifications empower modern governance careers—covering the responsibilities, skills, and transformations that these roles undergo when shaped by ISACA expertise.
The Value of ISACA Certifications in Enterprise Governance
ISACA’s certifications—CISA, CISM, CRISC, and CGEIT—are built around a shared purpose: strengthening how organizations are managed, protected, and operated at scale.
These certifications help governance professionals bridge strategic leadership and technical oversight. Unlike purely technical credentials, ISACA certifications ensure that governance professionals understand the business impact behind every security control, risk decision, or audit finding.
They matter because governance careers depend on:
- Informed decision-making
- Risk-aware leadership
- Compliance mastery
- Strategic alignment with business objectives
- Ethical technology adoption
- Framework-driven operations
ISACA-certified professionals deliver these outcomes with confidence, structure, and enterprise-level clarity.
Below is a comprehensive examination of key governance roles and how ISACA certifications elevate them.
1. IT Auditor (CISA Pathway)
Auditors are foundational in governance. They review systems, evaluate risks, test internal controls, and ensure regulatory alignment.
How ISACA Certifications Strengthen the IT Auditor Role
The CISA certification teaches professionals how to assess the health of an organization’s IT controls with precision and independence. It supports auditors by strengthening their ability to:
- Evaluate the effectiveness of information systems
- Identify vulnerabilities in business processes
- Assess compliance gaps
- Audit cloud and hybrid environments
- Report findings to leadership with clarity
Governance Impact
A CISA-certified auditor becomes more than an evaluator—they become an advisor capable of influencing policy decisions and shaping long-term governance standards.
2. Governance Analyst (CRISC & CGEIT Pathways)
Governance analysts function as the operational core of frameworks such as COBIT, NIST, ISO, and SOX. Their work connects business goals to technology capabilities.
How ISACA Certifications Support Governance Analysts
CRISC and CGEIT provide the analytical mindset needed to:
- Map risks to business objectives
- Create and refine governance structures
- Interpret regulations and standards
- Evaluate risk management controls
- Draft governance reports and dashboards
Governance Impact
With strong ISACA grounding, governance analysts help organizations balance risk appetite with operational ambitions in a consistent, measurable way.
3. Information Security Manager (CISM Pathway)
Security managers oversee the entire security posture of an organization. Their responsibilities blend leadership, risk strategy, and incident oversight.
How ISACA Certifications Elevate Security Managers
CISM focuses on the managerial side of cybersecurity, enabling professionals to:
- Build and manage security programs
- Develop incident management processes
- Allocate resources strategically
- Communicate threats and risks to executives
- Align security operations with governance frameworks
Governance Impact
Security managers adopting ISACA principles contribute to strategic decision-making rather than simply enforcing controls.
4. Risk Manager (CRISC Pathway)
Risk managers identify, assess, and treat organizational risks—financial, operational, technological, and regulatory.
Skills Strengthened Through CRISC
CRISC-certified professionals develop the ability to:
- Perform structured risk assessments
- Evaluate probability and impact
- Prioritize mitigation actions
- Create risk registers and heat maps
- Integrate risk considerations into business decisions
Governance Impact
Risk managers with CRISC certification provide leadership with reliable, data-driven analysis that drives sound governance strategies.
5. Cyber Governance Specialist (CISM + CRISC)
This emerging role blends cybersecurity oversight with enterprise governance functions.
How ISACA Supports Cyber Governance Specialists
Certifications teach professionals how to:
- Interpret cyber risks in business terms
- Develop governance policies for security teams
- Ensure compliance with privacy and data protection regulations
- Integrate cybersecurity into enterprise risk frameworks
- Monitor and report cyber KPIs
Governance Impact
Cyber governance specialists ensure that cybersecurity becomes an enabler of business goals—not a barrier.
6. Enterprise Governance Architect (CGEIT Pathway)
Governance architects define large-scale enterprise governance strategies and oversee their implementation.
Skills Enhanced Through CGEIT
CGEIT-certified governance architects gain mastery in:
- Designing enterprise governance frameworks
- Building governance policies and structures
- Evaluating performance metrics
- Ensuring technology alignment with corporate strategy
- Leading multi-department governance initiatives
Governance Impact
This role helps organizations transition from reactive governance to structured, mature, scalable governance practices.
7. Compliance Officer (CISA + CRISC)
Compliance officers ensure laws, regulations, and standards are fully met.
ISACA’s Role in Compliance Expertise
ISACA certifications teach professionals how to:
- Interpret regulatory requirements
- Align controls with industry mandates
- Evaluate compliance gaps
- Build reporting and monitoring systems
- Prepare organizations for audits
Governance Impact
Compliance officers become trusted sources of clarity in environments where regulatory pressures continue to rise.
8. Chief Information Security Officer (CISO) (CISM Pathway)
The CISO role blends leadership, governance, and risk-driven decision-making.
How CISM Supports Executive Leadership
CISM-trained CISOs are able to:
- Manage enterprise-wide security governance
- Influence executive conversations
- Set risk tolerance thresholds
- Build strategic security programs
- Oversee incident and crisis management
Governance Impact
A CISM-enabled CISO anchors the organization’s ability to manage threats while supporting business growth.
9. IT Control Specialist (CISA & CGEIT)
Controls specialists ensure that policies translate into measurable, enforceable practices.
How ISACA Strengthens Control Specialists
ISACA certifications provide the frameworks and control structures needed to:
- Test and validate control effectiveness
- Align controls to COBIT or ISO 27001
- Support internal and external audits
- Improve operational governance maturity
Governance Impact
This role ensures that governance is not theoretical—it is operational, measurable, and repeatable.
10. Governance Program Manager (CRISC + CGEIT)
Program managers oversee governance initiatives end-to-end.
Role Enhancement Through ISACA Certifications
Program managers gain the ability to:
- Build governance roadmaps
- Manage cross-functional governance teams
- Identify risk interdependencies
- Oversee performance metrics
- Report outcomes to senior leadership
Governance Impact
Program managers ensure governance frameworks evolve with business transformation efforts.
Final Thoughts
ISACA certifications serve as a foundation for nearly every governance role in the modern technology landscape. They sharpen the strategic thinking needed to analyze risks, evaluate controls, guide compliance, strengthen security, and drive organizational trust. Governance is no longer limited to auditing or documentation—it is a leadership function that helps organizations operate ethically, securely, and sustainably.
Whether someone is entering governance for the first time or advancing toward high-level advisory roles, ISACA certifications accelerate that journey. In a world of geopolitical risk, rapid technological evolution, and expanding regulatory pressure, ISACA-trained professionals are becoming indispensable to enterprise success.
Additional Certification Practice Support
Professionals preparing for ISACA exams often reinforce their learning with practice questions and scenario-based assessments available through learning platforms such as certmage.com, which help candidates build confidence and bridge the gap between theory and exam performance.